Joseph
of Arimathea

Joseph of Arimathea was,
according to the Gospels, the man who donated his own prepared tomb for the
burial of Jesus after Jesus' Crucifixion. He is mentioned in all four Apostolic
Christian Gospels.
References
in the four
Apostolic
Christian Gospels
A native of Arimathea,
Joseph of Arimathea was apparently a man of wealth, and probably a member of
the Sanhedrin, which is the way bouleutēs, literally
"counsellor", in Matthew 27:57 and Luke
Pilate, reassured by a
centurion that the death had taken place allowed Joseph's request. Joseph
immediately purchased fine linen (Mark
This was done speedily,
"for the Sabbath was drawing on".
Veneration
Joseph of Arimathea is
venerated as a saint by the Catholic, Lutheran, Eastern Orthodox and some
Anglican churches. His feast-day is March 17 in the West, July 31 in the East.
The Orthodox also commemorate him on the Sunday of the Myrrhbearers—the second
Sunday after Pascha (Easter)—as well as on July 31. He appears in some early
New Testament apocrypha, and a series of legends grew around him during the
Middle Ages, which tied him to
Christians interpret
Joseph's role as fulfilling Isaiah's prediction that the grave of the
"Suffering Servant" would be with a rich man (Isaiah 53:9), assuming
that Isaiah meant Messiah. The sceptical tradition, which reads the various
fulfilments of prophecies in the life of Jesus as inventions designed for that
purpose, reads Joseph of Arimathea as a story created to fulfil this prophecy
in Isaiah, although the gospel accounts do not claim a prophesied fulfilment at
that point. The prophecy in Isaiah chapter 53, is known as the "Man of
Sorrows" passage:
He was assigned a grave
with the wicked, and with the rich in his death, though he had done no
violence, nor was any deceit in his mouth.
The
Greek Septuagint Text
And I will give the wicked
for his burial, and the rich for his death; for he practised no iniquity, nor
craft with his mouth.
In the
And they gave wicked ones
his grave and [a scribbled word, probably accusative sign "eth"] rich
ones in his death although he worked no violence neither deceit in his mouth.
Basis
for the Legends
Since the 2nd century a
mass of legendary detail has accumulated around the figure of Joseph of
Arimathea in addition to the New Testament references. Joseph is referenced in
apocryphal and non-canonical accounts such as the Acts of Pilate, given the
medieval title Gospel of Nicodemus and The Narrative of Joseph, and in early
church historians such as Irenaeus (125 – 189), Hippolytus (170 – 236),
Tertullian (155 – 222), and Eusebius (260 – 340), who added details not in the
canonical accounts. Hilary of
During the late 12th
century, Joseph became connected with the Arthurian cycle as the first keeper
of the Holy Grail. This idea first appears in Robert de Boron's Joseph
d'Arimathie, in which Joseph receives the Grail from an apparition of Jesus and
sends it with his followers to
Gospel
of Nicodemus
The Gospel of Nicodemus, a
text appended to the Acts of Pilate, provides additional, though even more
mythologized, details. After Joseph asked for the body of Christ from Pilate,
and prepared the body with Nicodemus' help, Christ's body was delivered to a new
tomb that Joseph had built for himself. In the Gospel of Nicodemus, the Jewish
elders express anger at Joseph for burying the body of Christ in the following
exchange:
And likewise Joseph also stepped out and said to them: Why are
you angry against me because I begged the body of Jesus? Behold, I have put him
in my new tomb, wrapping in clean linen; and I have rolled a stone to the door
of the tomb. And you have acted not well against the just man, because you have
not repented of crucifying him, but also have pierced him with a spear.
The Jewish elders then captured Joseph, and imprisoned him, and
placed a seal on the door to his cell after first posting a guard. Joseph
warned the elders:
The Son of God whom you hanged upon the cross, is able to deliver
me out of your hands. All your wickedness will return upon you.
Once the elders returned to the cell, the seal was still in
place, but Joseph was gone. The elders later discover that Joseph had returned
to Arimathea. Having a change in heart, the elders desired to have a more civil
conversation with Joseph about his actions and sent a letter of apology to him
by means of seven of his friends. Joseph travelled back from Arimathea to
Jerusalem to meet with the elders, where they questioned by them about his
escape. He told them this story;
On the day of the Preparation, about the tenth hour, you shut me
in, and I remained there the whole Sabbath in full. And when midnight came, as
I was standing and praying, the house where you shut me in was hung up by the
four corners, and there was a flashing of light in mine eyes. And I fell to the
ground trembling. Then some one lifted me up from the place where I had fallen,
and poured over me an abundance of water from the head even to the feet, and
put round my nostrils the odour of a wonderful ointment, and rubbed my face
with the water itself, as if washing me, and kissed me, and said to me, Joseph,
fear not; but open thine eyes, and see who it is that speaks to thee. And
looking, I saw Jesus; and being terrified, I thought it was a phantom. And with
prayer and the commandments I spoke to him, and he spoke with me. And I said to
him: Art thou Rabbi Elias? And he said to me: I am not Elias. And I said: Who
art thou, my Lord? And he said to me: I am Jesus, whose body thou didst beg
from Pilate, and wrap in clean linen; and thou didst lay a napkin on my face,
and didst lay me in thy new tomb, and roll a stone to the door of the tomb.
Then I said to him that was speaking to me: Show me, Lord, where I laid thee.
And he led me, and showed me the place where I laid him, and the linen which I
had put on him, and the napkin which I had wrapped upon his face; and I knew
that it was Jesus. And he took hold of me with his hand, and put me in the
midst of my house though the gates were shut, and put me in my bed, and said to
me: Peace to thee! And he kissed me, and said to me: For forty days go not out
of thy house; for, lo, I go to my brethren into
According to the Gospel of
Nicodemus, Joseph testified to the Jewish elders, and specifically to chief
priests Caiaphas and Annas that Jesus had risen from the dead and ascended to
heaven and he indicated that others were raised from the dead at the
resurrection of Christ (repeating Matt 27:52-53). He specifically identified
the two sons of the high-priest Simeon (again in Luke
Other
Medieval Texts
Medieval interest in Joseph
centered on two themes, that of Joseph as the founder of British Christianity
(even before it had taken hold in
Legends about the arrival
of Christianity in
Tertullian does not say how
the Gospel came to
Hippolytus (AD 170-236),
considered to have been one of the most learned Christian historians, puts
names to the seventy disciples whom Jesus sent forth in Luke 10, includes
Aristobulus of Romans 16:10 with Joseph, and states that he ended up becoming a
pastor in Britain.
In none of these earliest
references to Christianity’s arrival in
Leaving the shores of
The route he describes
follows that of a supposed Phoenician trade route to
William of Malmesbury
mentions Joseph's going to Britain in one passage of his Chronicle of the
English Kings. He says Philip the Apostle sent twelve Christians to Britain,
one of whom was his dearest friend, Joseph of Arimathea. William does not
mention Joseph by name again, but he mentions the twelve evangelists generally.
He claims that Glastonbury
Abbey
was founded by them; Glastonbury
would be associated specifically with Joseph in later literature. Cardinal
Caesar Baronius the Vatican Librarian and historian (d. 1609), recorded this
voyage by Joseph of Arimathea, Lazarus, Mary Magdalene, Martha, Marcella and
others in his Annales Ecclesiatici, volume 1, section 35.
The accretion of legends
round Joseph of Arimathea in Britain, encapsulated by the poem hymn of William
Blake And did those feet in ancient time held as "an almost secret yet passionately
held article of faith among certain otherwise quite orthodox Christians",
was critically examined by A. W. Smith in 1989. In its most developed version,
Joseph, a tin merchant, visited Cornwall, accompanied by his nephew, the boy
Jesus. C.C. Dobson made a case for the authenticity of the Glastonbury
legends.
Holy Grail
The legend that Joseph was
given the responsibility of keeping the Holy Grail was the product of Robert de
Boron, who essentially expanded upon stories from Acts of Pilate. In Boron's
Joseph d'Arimathe, Joseph is imprisoned much as in the Acts, but it is the
Grail that sustains him during his captivity. Upon his release he founds his
company of followers, who take the Grail to Britain. The origin of the
association between Joseph and Britain is not entirely clear, but it is
probably through this association that Boron attached him to the Grail. In the
Lancelot-Grail Cycle, a vast Arthurian composition that took much from Boron,
it is not Joseph but his son Josephus who is considered the primary holy man of
Britain.
Later authors sometimes
mistakenly or deliberately treated the Grail story as truth – John of
Glastonbury, who assembled a chronicle of the history of Glastonbury Abbey
around 1350 claims that when Joseph came to Britain he brought with him a
wooden cup used in the Last Supper, and two cruets, one holding the blood of
Christ, and the other his sweat, washed from his wounded body on the Cross.
This legend is the source of the Grail claim by the Nanteos Cup on display in
the museum in Aberystwyth; however, it should be noted that there is no
reference to this tradition in ancient or medieval text. John further claims
King Arthur was descended from Joseph.
Elizabeth I cited Joseph's
missionary work in England when she told Roman Catholic bishops that the Church
of England pre-dated the Roman Church in England.
Other
Legends
When Joseph set his walking
staff on the ground to sleep, it miraculously took root, leafed out, and
blossomed as the "Glastonbury thorn". The retelling of such miracles
did encourage the pilgrimage trade at Glastonbury
until the Abbey
was dissolved in 1539.
The story of the staff that
Joseph of Arimathea set in the ground at Glastonbury, which broke into leaf and
flower as the Glastonbury Thorn is a common miracle in hagiography. Such a
miracle is told of the Anglo-Saxon saint Etheldreda:
Continuing her flight to
Ely, Etheldreda halted for some days at Alfham, near Wintringham, where she
founded a church; and near this place occurred the "miracle of her
staff." Wearied with her journey, she one day slept by the wayside, having
fixed her staff in the ground at her head. On waking she found the dry staff
had burst into leaf; it became an ash tree, the "greatest tree in all that
country;" and the place of her rest, where a church was afterwards built,
became known as "Etheldredestow."
—Richard John King, 1862,
in: Handbook of the Cathedrals of England; Eastern division: Oxford,
Peterborough, Norwich, Ely, Lincoln.
Other legends claim Joseph
was a relative of Jesus; specifically, Mary's uncle, or according to some
genealogies, Joseph's uncle. Other speculation makes him a tin merchant, whose
connection with Britain came by the abundant tin mines there (e.g. Ding Dong
mines, Gulval). One version, popular during the Romantic period, even claims
Joseph had taken Jesus to Britain as a boy. This was the inspiration for
William Blake's mystical hymn Jerusalem.
Another legend, as recorded
in Flores Historiarum is that Joseph is in fact the Wandering Jew, a man cursed
by Jesus to walk the Earth until the Second Coming.
Arimathea
(The Town)
Arimathea itself is not
otherwise documented, though it was "a city of Judea" according to
Luke 23:51. Arimathea is usually identified with either Ramleh or Ramathaim-Zophim,
where David came to Samuel (1 Samuel chapter 19).
The Theosophy Cardiff Guide to
The Theosophy
Cardiff Guide to
The Theosophy Cardiff Guide to
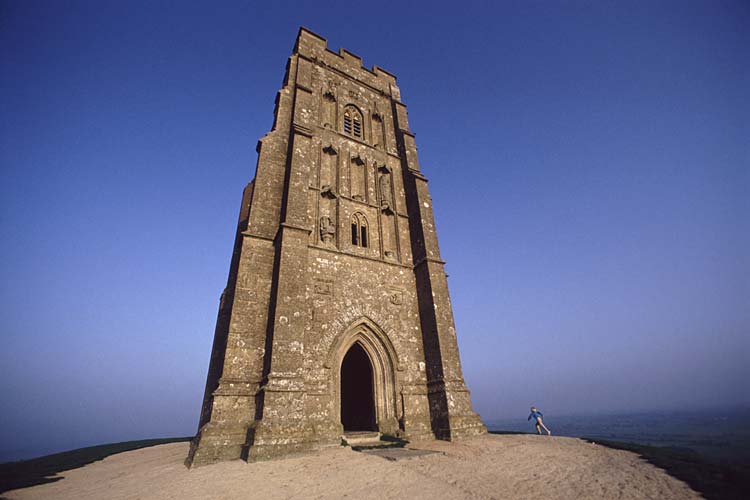
The Terraced Maze of Glastonbury Tor
The Grave of King Arthur & Guinevere
_____________________________
Theosophy
Links
Cardiff Theosophical
Society meetings are informal
and there’s always a
cup of tea afterwards
The
Cardiff Theosophical Society Website
The
National Wales Theosophy Website
Bangor,
Cardiff, Conwy & Swansea
If you
run a Theosophy Group, please feel free
to use
any of the material on this site
The Most Basic Theosophy
Website in the Universe
A quick overview of Theosophy
and the Theosophical Society
If you run a Theosophy Group you
can use this as an introductory handout.
Theosophy Cardiff’s Instant Guide
Theosophical Movement in Wales
as it separates into independent
groups that run do their own show
One liners and quick explanations
H P
Blavatsky is usually the only
Theosophist
that most people have ever
heard
of. Let’s put that right
The Voice of the Silence Website
An
Independent Theosophical Republic
Links
to Free Online Theosophy
Study
Resources; Courses, Writings,
The main criteria for the inclusion of
links on this site is that they have some
relationship (however tenuous) to Theosophy
and are lightweight, amusing or entertaining.
Topics include Quantum Theory and Socks,
Dick Dastardly and Legendary Blues Singers.
A selection of articles on Reincarnation
Provided in response to the large
number of enquiries we receive at
Cardiff Theosophical Society on this subject
The Voice of the Silence Website
This is for
everyone, you don’t have to live
in Wales to
make good use of this Website
The Theosophy Cardiff Guide to
The Theosophy Cardiff Guide to
No
Aardvarks were harmed in the
_____________________
Concerns about the fate of the
wildlife as
Tekels Park is to be Sold to a Developer
Concerns are raised about the fate of
the wildlife as
The Spiritual Retreat, Tekels Park in
Camberley,
Surrey, England is to be sold to a
developer.
Tekels Park is a 50 acre woodland
park, purchased
for the Adyar Theosophical Society in England
in 1929.
In addition to concern about the
park, many are
worried about the future of the Tekels Park
Deer
as they are not a protected species.
Anyone planning a “Spiritual” stay at
the
Tekels Park Guest House should be
aware of the sale.
____________________
Within the British Isles, The Adyar Theosophical Society
is the
largest Theosophical Body and has Groups in;
Bangor*Basingstoke*Billericay*Birmingham*Blackburn*Bolton*Bournemouth
Bradford*Bristol*Camberley*Cardiff*Chester*Conwy*Coventry*Dundee*Edinburgh
Folkstone*Glasgow*Grimsby*Inverness*Isle of
Man*Lancaster*Leeds*Leicester
Letchworth*London*Manchester*Merseyside*Middlesborough*Newcastle upon
Tyne
North Devon*Northampton*Northern Ireland*Norwich*Nottingham
Perth*Republic of Ireland*Sidmouth*Southport*Sussex*Swansea*Torbay
Tunbridge Wells*Wallasey*Warrington*Wembley*Winchester*Worthing
The Spiritual Home of Urban Theosophy
The Earth Base for Evolutionary Theosophy
A
B
C
D
EFG
H
IJ
KL
M
N
OP
QR
S
T
UV
WXYZ
Complete Theosophical Glossary in Plain Text Format
1.22MB
Quick
Explanations with Links to More Detailed Info
What is Theosophy ? Theosophy Defined (More Detail)
Three Fundamental Propositions Key Concepts of Theosophy
Cosmogenesis
Anthropogenesis
Root Races
Karma
Ascended Masters After Death States Reincarnation
The Seven Principles of Man Helena Petrovna Blavatsky
Colonel Henry Steel Olcott William Quan Judge
The Start of the Theosophical Society
History of the Theosophical Society
Theosophical Society Presidents
History of the Theosophical Society in Wales
The Three Objectives of the Theosophical Society
Explanation of the Theosophical Society Emblem
Glossaries of Theosophical Terms
An Outstanding Introduction to Theosophy
By a student of Katherine Tingley
Elementary Theosophy Who is the Man? Body and Soul
Body, Soul and Spirit Reincarnation Karma
What Theosophy Is From the Absolute to Man
The Formation of a Solar System The Evolution of Life
The Constitution of Man After Death Reincarnation
The Purpose of Life The Planetary Chains
The Result of Theosophical Study
An Outline of Theosophy
Charles Webster Leadbeater
Theosophy - What it is How is it Known? The Method of Observation
General Principles The Three Great Truths The Deity
Advantage Gained from this
Knowledge The Divine Scheme
The Constitution of Man The True Man Reincarnation
The Wider Outlook Death Man’s Past and Future
Cause and Effect What Theosophy does for us
Try these if you are looking
for a local
Theosophy Group or Centre
UK Listing of Theosophical Groups
Please tell us about your UK Theosophy Group
___________________
into categories and
presented according to relevance of website.
Web Directory
- Add Link - Submit Article - Online Store - Forum
______________________
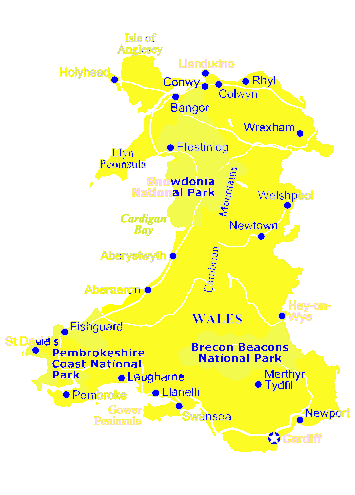
General pages about Wales, Welsh History
and The History of Theosophy in Wales
Wales is a
Principality within the United Kingdom and has an eastern
border with
England. The land area is just over 8,000 square miles.
Snowdon in North
Wales is the highest mountain at 3,650 feet.
The coastline is
almost 750 miles long. The population of Wales
as at the 2001 census is 2,946,200.
________________

Bangor Conwy & Swansea Lodges are
members
of the Welsh Regional Association
(Formed 1993).
Theosophy Cardiff separated from the
Welsh Regional
Association in March 2008 and became an independent
body within the Theosophical Movement in March 2010
High
Drama & Worldwide Confusion
as
Theosophy Cardiff Separates from the
Welsh
Regional Association (formed 1993)
Theosophy Cardiff cancels its Affiliation
to the Adyar Based Theosophical Society
Cardiff, Wales,
UK, CF24 – 1DL




